Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) isn’t a new vulnerability. It’s persistent, versatile, and still very effective in real-world exploitation. Even mature applications fail against it. Most scanners attack XSS like a toddler with a keyboard: repeated payloads, random fuzzing, pure noise.
XSStrike offers improved testing by analyzing responses, understanding injection context, and generating effective payloads. This offers pentesters more accurate results and real exploitation paths.
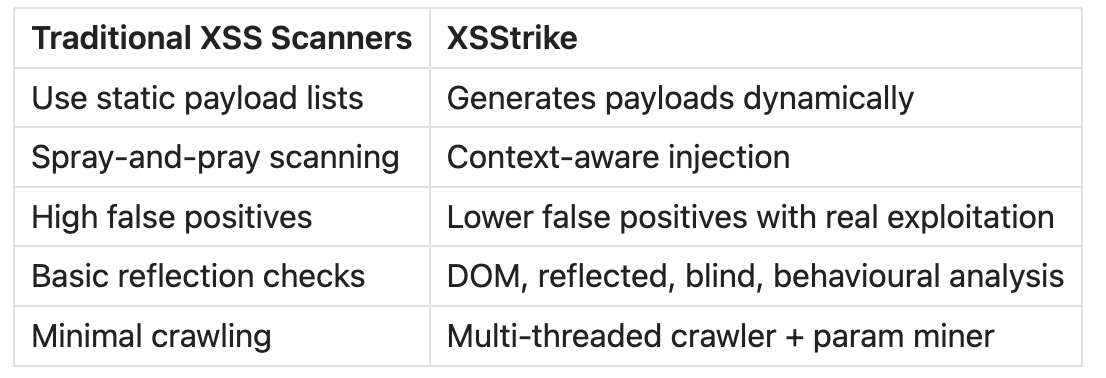
What Makes XSStrike Special?
Most scanners send fixed payload lists and hope one slips past filters. XSStrike:
This difference matters. In bug bounty or red team ops, precision beats volume. A single correct payload is worth more than 10,000 requests.
How XSStrike Actually Works
This is where this tool becomes interesting. XSStrike uses:
Four Handmade Parsers
These help XSStrike understand how input flows into the response:
HTML parser
JavaScript parser
Attribute context parser
Event handler parser
Instead of just noticing reflection, it checks where it’s reflected—script block, tag attribute, DOM sink, inline JS, etc.—then tailors payloads to match.
Intelligent Payload Generator
Once reflection is detected, it:
Determines the breaking point injections
Bypasses escaping
Generates working payloads for that context
Chains payload encodings if needed
This dramatically reduces false positives. You don’t just detect XSS—you exploit it.
Behavioral + Fuzzing Engine
XSStrike mutates payloads to trigger execution paths like:
Closing tags
Breaking attribute blocks
Triggering bypasses like case-switching, newline injection, JS event abuse
If it hits something executable, you’re done.
A Workflow Using XSStrike
Here’s how you would realistically use XSStrike during an engagement:
Step 1 — Quick Reflected XSS Test
python xsstrike.py -u “https://target.com/page?input=test”
This checks basic reflection paths and reports vulnerable injection points.
Step 2 — Deep Parameter Discovery
python xsstrike.py -u “https://target.com” --crawl
Useful for hidden parameters, form inputs, and deep routes—very common in real apps.
Step 3 — Bruteforce Payload Variants
python xsstrike.py -u “https://target.com” --payload payloads.txt
You can feed your own payload stash. Good for WAF bypass games.
Step 4 — DOM XSS Hunting
Single-page apps love to hide client-side bugs. XSStrike hunts them.
python xsstrike.py -u “https://target.com” --fuzz --crawl
Step 5 — Blind XSS Support
If the app stores and later renders the payload:
Insert payload crafted by XSStrike
Wait for your callback platform to trigger
Useful for admin panels and delayed execution.
🥷 WAF Detection + Bypass Tricks
XSStrike includes WAF signatures extracted from sqlmap. It identifies:
Cloudflare
ModSecurity
Incapsula
AWS WAF
Custom enterprise rulesets
Once detected, it mutates payloads to slip past filtering.
Example bypass patterns XSStrike plays with:
</ScrIpT><svg/onload=confirm(1)>
<A/oNmoUseOver%0d=%0d[8].find(alert)>click
</tItLe/onPoIntErEnter=(prompt`xsstrike`)>
These payloads change case, insert whitespace, abuse event handlers, and break tag boundaries.
Delightful chaos.
Real-World Attack Scenarios Where XSStrike Shines
If your target filters <script>, XSStrike will happily respond with 200 alternatives.
Limitations You Should Know
No tool is magic. XSStrike is powerful, but:
low when scanning gigantic SPA applications
Requires thinking instead of point-and-click laziness
Not built for enterprise crawling scale like Burp Pro
This is a weapon for skilled attackers, not a one-button exploit.
If you want a scanner that actually understands XSS, XSStrike is a must-have tool for pentesters. Context-aware payload generation, DOM support, WAF bypassing, and deep fuzzing make it more capable than most open-source scanners in the wild.
🔗 GitHub Project: https://github.com/s0md3v/XSStrike